Finding Content
PDFDancer provides flexible selection methods to find content in your PDF documents. You can select all elements of a type, find elements at specific positions, or search by text content. All selection methods work at both document and page level.
Document-Level vs Page-Level Selection
Every selection method can search across the entire document or limit to a specific page:
- Python
- TypeScript
- Java
from pdfdancer import PDFDancer
with PDFDancer.open("document.pdf") as pdf:
# Document-level: searches ALL pages
all_paragraphs = pdf.select_paragraphs()
# Page-level: searches only page 0
page_paragraphs = pdf.page(1).select_paragraphs()
import { PDFDancer } from 'pdfdancer-client-typescript';
const pdf = await PDFDancer.open('document.pdf');
// Document-level: searches ALL pages
const allParagraphs = await pdf.selectParagraphs();
// Page-level: searches only page 0
const pageParagraphs = await pdf.page(1).selectParagraphs();
import com.tfc.pdf.pdfdancer.api.PDFDancer;
import com.tfc.pdf.pdfdancer.api.common.model.*;
PDFDancer pdf = PDFDancer.createSession("document.pdf");
// Document-level: searches ALL pages
List<Paragraph> allParagraphs = pdf.selectParagraphs();
// Page-level: searches only page 0
List<Paragraph> pageParagraphs = pdf.page(1).selectParagraphs();
1. Select All Elements
Get all elements of a specific type from the document or page.
Available Content Types
- Python
- TypeScript
- Java
with PDFDancer.open("document.pdf") as pdf:
# Text content
all_paragraphs = pdf.select_paragraphs()
all_lines = pdf.select_text_lines() # or select_lines()
# Visual content
all_images = pdf.select_images()
all_paths = pdf.select_paths() # vector graphics
all_forms = pdf.select_forms() # form XObjects (templates, watermarks)
# Interactive content
all_fields = pdf.select_form_fields() # AcroForm fields
# Page-scoped selections
page_paragraphs = pdf.page(1).select_paragraphs()
page_images = pdf.page(1).select_images()
const pdf = await PDFDancer.open('document.pdf');
// Text content
const allParagraphs = await pdf.selectParagraphs();
const allLines = await pdf.selectTextLines(); // or selectLines()
// Visual content
const allImages = await pdf.selectImages();
const allPaths = await pdf.selectPaths(); // vector graphics
const allForms = await pdf.selectForms(); // form XObjects (templates, watermarks)
// Interactive content
const allFields = await pdf.selectFormFields(); // AcroForm fields
// Page-scoped selections
const pageParagraphs = await pdf.page(1).selectParagraphs();
const pageImages = await pdf.page(1).selectImages();
PDFDancer pdf = PDFDancer.createSession("document.pdf");
// Text content
List<Paragraph> allParagraphs = pdf.selectParagraphs();
List<TextLine> allLines = pdf.selectTextLines(); // or selectLines()
// Visual content
List<Image> allImages = pdf.selectImages();
List<Path> allPaths = pdf.selectPaths(); // vector graphics
List<FormXObject> allForms = pdf.selectForms(); // form XObjects (templates, watermarks)
// Interactive content
List<FormField> allFields = pdf.selectFormFields(); // AcroForm fields
// Page-scoped selections
List<Paragraph> pageParagraphs = pdf.page(1).selectParagraphs();
List<Image> pageImages = pdf.page(1).selectImages();
Select All Elements (Convenience Method)
Use select_elements() to get all content types at once:
- Python
- TypeScript
- Java
with PDFDancer.open("document.pdf") as pdf:
# Get all elements in the entire document
# Returns paragraphs, text lines, images, paths, forms, and form fields
all_elements = pdf.select_elements()
# Get all elements on a specific page
page_elements = pdf.page(1).select_elements()
# Process all elements
for element in page_elements:
print(f"Type: {element.object_type}, Position: ({element.position.x}, {element.position.y})")
const pdf = await PDFDancer.open('document.pdf');
// Get all elements in the entire document
// Returns paragraphs, text lines, images, paths, forms, and form fields
const allElements = await pdf.selectElements();
// Get all elements on a specific page
const pageElements = await pdf.page(1).selectElements();
// Process all elements
for (const element of pageElements) {
console.log(`Type: ${element.type}, Position: (${element.position.x}, ${element.position.y})`);
}
PDFDancer pdf = PDFDancer.createSession("document.pdf");
// Get all elements in the entire document
// Returns paragraphs, text lines, images, paths, forms, and form fields
List<Element> allElements = pdf.selectElements();
// Get all elements on a specific page
List<Element> pageElements = pdf.page(1).selectElements();
// Process all elements
for (Element element : pageElements) {
System.out.println("Type: " + element.getType() + ", Position: (" +
element.getPosition().getX() + ", " + element.getPosition().getY() + ")");
}
Working with Selected Elements
All selection methods return lists/arrays of typed objects with methods and properties:
- Python
- TypeScript
- Java
with PDFDancer.open("document.pdf") as pdf:
# Select and inspect
paragraphs = pdf.page(1).select_paragraphs()
for para in paragraphs:
print(f"Text: {para.text}")
print(f"Font: {para.font_name} at {para.font_size}pt")
print(f"Position: ({para.position.x()}, {para.position.y()})")
# Select and manipulate
images = pdf.select_images()
for img in images:
print(f"Image at ({img.position.x()}, {img.position.y()})")
# Objects have .delete(), .move_to(), etc.
# Select and check form fields
fields = pdf.select_form_fields()
for field in fields:
print(f"{field.field_name}: {field.value}")
const pdf = await PDFDancer.open('document.pdf');
// Select and inspect
const paragraphs = await pdf.page(1).selectParagraphs();
for (const para of paragraphs) {
console.log(`Text: ${para.text}`);
console.log(`Font: ${para.fontName} at ${para.fontSize}pt`);
console.log(`Position: (${para.position.x}, ${para.position.y})`);
}
// Select and manipulate
const images = await pdf.selectImages();
for (const img of images) {
console.log(`Image at (${img.position.x}, ${img.position.y})`);
// Objects have .delete(), .moveTo(), etc.
}
// Select and check form fields
const fields = await pdf.selectFormFields();
for (const field of fields) {
console.log(`${field.fieldName}: ${field.value}`);
}
PDFDancer pdf = PDFDancer.createSession("document.pdf");
// Select and inspect
List<Paragraph> paragraphs = pdf.page(1).selectParagraphs();
for (Paragraph para : paragraphs) {
System.out.println("Text: " + para.getText());
System.out.println("Font: " + para.getFontName() + " at " + para.getFontSize() + "pt");
System.out.println("Position: (" + para.getPosition().getX() + ", " + para.getPosition().getY() + ")");
}
// Select and manipulate
List<Image> images = pdf.selectImages();
for (Image img : images) {
System.out.println("Image at (" + img.getPosition().getX() + ", " + img.getPosition().getY() + ")");
// Objects have .delete(), .moveTo(), etc.
}
// Select and check form fields
List<FormField> fields = pdf.selectFormFields();
for (FormField field : fields) {
System.out.println(field.getFieldName() + ": " + field.getValue());
}
2. Select by Position
Find elements at specific x, y coordinates on a page. Useful when you know the layout structure.
Selecting at Coordinates
- Python
- TypeScript
- Java
with PDFDancer.open("document.pdf") as pdf:
# Find paragraphs at specific coordinates
header = pdf.page(1).select_paragraphs_at(x=72, y=750)
# Find images at logo position
logo = pdf.page(1).select_images_at(x=50, y=750)
# Find form fields at signature area
signature = pdf.page(2).select_form_fields_at(x=150, y=100)
# Find paths (vector graphics) at specific position
lines = pdf.page(1).select_paths_at(x=200, y=400)
# Find form XObjects at watermark position
watermark = pdf.page(1).select_forms_at(x=300, y=400)
# Find text lines at specific coordinates
date_line = pdf.page(1).select_text_lines_at(x=500, y=750)
const pdf = await PDFDancer.open('document.pdf');
// Find paragraphs at specific coordinates
const header = await pdf.page(1).selectParagraphsAt(72, 750);
// Find images at logo position
const logo = await pdf.page(1).selectImagesAt(50, 750);
// Find form fields at signature area
const signature = await pdf.page(2).selectFormFieldsAt(150, 100);
// Find paths (vector graphics) at specific position
const lines = await pdf.page(1).selectPathsAt(200, 400);
// Find form XObjects at watermark position
const watermark = await pdf.page(1).selectFormsAt(300, 400);
// Find text lines at specific coordinates
const dateLine = await pdf.page(1).selectTextLinesAt(500, 750);
PDFDancer pdf = PDFDancer.createSession("document.pdf");
// Find paragraphs at specific coordinates
List<Paragraph> header = pdf.page(1).selectParagraphsAt(72, 750);
// Find images at logo position
List<Image> logo = pdf.page(1).selectImagesAt(50, 750);
// Find form fields at signature area
List<FormField> signature = pdf.page(2).selectFormFieldsAt(150, 100);
// Find paths (vector graphics) at specific position
List<Path> lines = pdf.page(1).selectPathsAt(200, 400);
// Find form XObjects at watermark position
List<FormXObject> watermark = pdf.page(1).selectFormsAt(300, 400);
// Find text lines at specific coordinates
List<TextLine> dateLine = pdf.page(1).selectTextLinesAt(500, 750);
Practical Example: Fixed Layout Documents
- Python
- TypeScript
- Java
with PDFDancer.open("invoice.pdf") as pdf:
# Invoice header is always at (72, 750)
header = pdf.page(1).select_paragraphs_at(72, 750)
if header:
print(f"Invoice: {header[0].text}")
# Total amount always at (450, 150)
total = pdf.page(1).select_paragraphs_at(450, 150)
if total:
print(f"Total: {total[0].text}")
# Company logo always at (50, 750)
logo = pdf.page(1).select_images_at(50, 750)
if logo:
print(f"Found logo at expected position")
const pdf = await PDFDancer.open('invoice.pdf');
// Invoice header is always at (72, 750)
const header = await pdf.page(1).selectParagraphsAt(72, 750);
if (header.length > 0) {
console.log(`Invoice: ${header[0].text}`);
}
// Total amount always at (450, 150)
const total = await pdf.page(1).selectParagraphsAt(450, 150);
if (total.length > 0) {
console.log(`Total: ${total[0].text}`);
}
// Company logo always at (50, 750)
const logo = await pdf.page(1).selectImagesAt(50, 750);
if (logo.length > 0) {
console.log('Found logo at expected position');
}
PDFDancer pdf = PDFDancer.createSession("invoice.pdf");
// Invoice header is always at (72, 750)
List<Paragraph> header = pdf.page(1).selectParagraphsAt(72, 750);
if (!header.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Invoice: " + header.get(0).getText());
}
// Total amount always at (450, 150)
List<Paragraph> total = pdf.page(1).selectParagraphsAt(450, 150);
if (!total.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Total: " + total.get(0).getText());
}
// Company logo always at (50, 750)
List<Image> logo = pdf.page(1).selectImagesAt(50, 750);
if (!logo.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Found logo at expected position");
}
Visual Example: Coordinate-Based Selection
See how PDFDancer finds elements at specific X,Y coordinates:
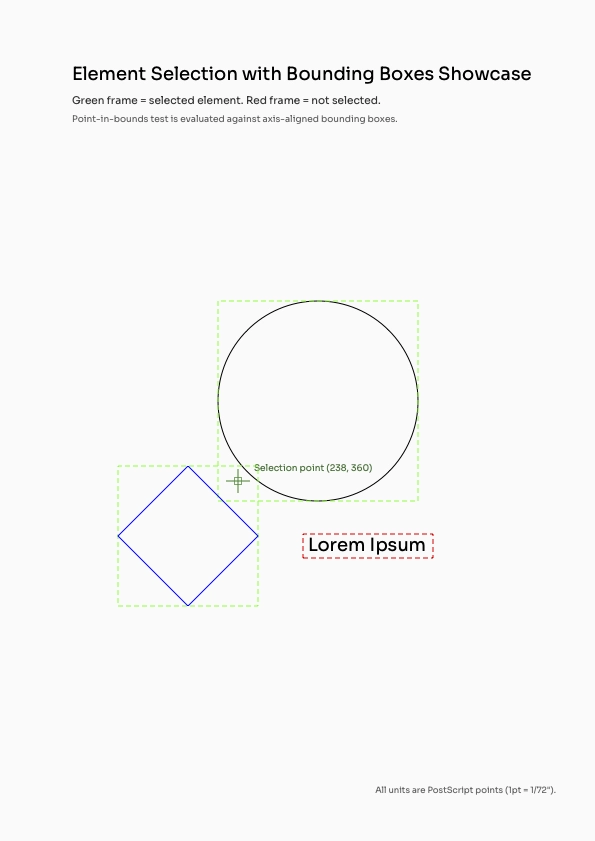
3. Select by Content
Search for text elements by their content using text matching or regular expressions.
Select by Text Prefix
Find paragraphs or text lines that start with specific text. You can search across the entire document or limit the search to a specific page.
- Python
- TypeScript
- Java
with PDFDancer.open("invoice.pdf") as pdf:
# Document-level search (searches all pages)
invoices = pdf.select_paragraphs_starting_with("Invoice #")
totals = pdf.select_paragraphs_starting_with("Total:")
disclaimers = pdf.select_paragraphs_starting_with("Note:")
# Find text lines by prefix across all pages
date_lines = pdf.select_text_lines_starting_with("Date:")
amount_lines = pdf.select_text_lines_starting_with("Amount:")
# Page-scoped prefix search (only searches specific page)
page_headers = pdf.page(1).select_paragraphs_starting_with("Executive Summary")
const pdf = await PDFDancer.open('invoice.pdf');
// Document-level search (searches all pages)
const invoices = await pdf.selectParagraphsStartingWith('Invoice #');
const totals = await pdf.selectParagraphsStartingWith('Total:');
const disclaimers = await pdf.selectParagraphsStartingWith('Note:');
// Find text lines by prefix across all pages
const dateLines = await pdf.selectTextLinesStartingWith('Date:');
const amountLines = await pdf.selectTextLinesStartingWith('Amount:');
// Page-scoped prefix search (only searches specific page)
const pageHeaders = await pdf.page(1).selectParagraphsStartingWith('Executive Summary');
PDFDancer pdf = PDFDancer.createSession("invoice.pdf");
// Document-level search (searches all pages)
List<Paragraph> invoices = pdf.selectParagraphsStartingWith("Invoice #");
List<Paragraph> totals = pdf.selectParagraphsStartingWith("Total:");
List<Paragraph> disclaimers = pdf.selectParagraphsStartingWith("Note:");
// Find text lines by prefix across all pages
List<TextLine> dateLines = pdf.selectTextLinesStartingWith("Date:");
List<TextLine> amountLines = pdf.selectTextLinesStartingWith("Amount:");
// Page-scoped prefix search (only searches specific page)
List<Paragraph> pageHeaders = pdf.page(1).selectParagraphsStartingWith("Executive Summary");
Select by Pattern (Regex)
Use regular expressions to find text matching complex patterns. Pattern matching works at both document and page levels.
All SDKs use Java-compatible regular expression syntax as defined in the Java Pattern class. Common patterns work the same across Python, TypeScript, and Java.
- Python
- TypeScript
- Java
import re
with PDFDancer.open("document.pdf") as pdf:
# Document-level pattern matching (searches all pages)
# Find dates in format YYYY-MM-DD
dates = pdf.select_paragraphs_matching(r"\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}")
# Find email addresses
emails = pdf.select_paragraphs_matching(r"[\w\.-]+@[\w\.-]+\.\w+")
# Find dollar amounts
prices = pdf.select_paragraphs_matching(r"\$\d+\.\d{2}")
# Find phone numbers
phones = pdf.select_text_lines_matching(r"\(\d{3}\) \d{3}-\d{4}")
# Find ZIP codes
zips = pdf.select_text_lines_matching(r"\d{5}(-\d{4})?")
# Find invoice numbers (custom pattern)
invoice_nums = pdf.select_paragraphs_matching(r"INV-\d{6}")
# Page-scoped pattern matching (only searches specific page)
page_dates = pdf.page(1).select_paragraphs_matching(r"\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}")
const pdf = await PDFDancer.open('document.pdf');
// Document-level pattern matching (searches all pages)
// Find dates in format YYYY-MM-DD
const dates = await pdf.selectParagraphsMatching('\\d{4}-\\d{2}-\\d{2}');
// Find email addresses
const emails = await pdf.selectParagraphsMatching('[\\w\\.-]+@[\\w\\.-]+\\.\\w+');
// Find dollar amounts
const prices = await pdf.selectParagraphsMatching('\\$\\d+\\.\\d{2}');
// Find phone numbers
const phones = await pdf.selectTextLinesMatching('\\(\\d{3}\\) \\d{3}-\\d{4}');
// Find ZIP codes
const zips = await pdf.selectTextLinesMatching('\\d{5}(-\\d{4})?');
// Find invoice numbers (custom pattern)
const invoiceNums = await pdf.selectParagraphsMatching('INV-\\d{6}');
// Page-scoped pattern matching (only searches specific page)
const pageDates = await pdf.page(1).selectParagraphsMatching('\\d{4}-\\d{2}-\\d{2}');
PDFDancer pdf = PDFDancer.createSession("document.pdf");
// Document-level pattern matching (searches all pages)
// Find dates in format YYYY-MM-DD
List<Paragraph> dates = pdf.selectParagraphsMatching("\\d{4}-\\d{2}-\\d{2}");
// Find email addresses
List<Paragraph> emails = pdf.selectParagraphsMatching("[\\w\\.-]+@[\\w\\.-]+\\.\\w+");
// Find dollar amounts
List<Paragraph> prices = pdf.selectParagraphsMatching("\\$\\d+\\.\\d{2}");
// Find phone numbers
List<TextLine> phones = pdf.selectTextLinesMatching("\\(\\d{3}\\) \\d{3}-\\d{4}");
// Find ZIP codes
List<TextLine> zips = pdf.selectTextLinesMatching("\\d{5}(-\\d{4})?");
// Find invoice numbers (custom pattern)
List<Paragraph> invoiceNums = pdf.selectParagraphsMatching("INV-\\d{6}");
// Page-scoped pattern matching (only searches specific page)
List<Paragraph> pageDates = pdf.page(1).selectParagraphsMatching("\\d{4}-\\d{2}-\\d{2}");
Select by Field Name
For form fields, you can select by the field's name:
- Python
- TypeScript
- Java
with PDFDancer.open("form.pdf") as pdf:
# Find specific form fields by name
signature_fields = pdf.select_form_fields_by_name("signature")
name_fields = pdf.select_form_fields_by_name("applicant_name")
date_fields = pdf.select_form_fields_by_name("application_date")
# Check and modify field values
if signature_fields:
sig = signature_fields[0]
print(f"Signature value: {sig.value}")
sig.edit().value("John Doe").apply()
const pdf = await PDFDancer.open('form.pdf');
// Find specific form fields by name
const signatureFields = await pdf.selectFormFieldsByName('signature');
const nameFields = await pdf.selectFormFieldsByName('applicant_name');
const dateFields = await pdf.selectFormFieldsByName('application_date');
// Check and modify field values
if (signatureFields.length > 0) {
const sig = signatureFields[0];
console.log(`Signature value: ${sig.value}`);
await sig.fill('John Doe');
}
PDFDancer pdf = PDFDancer.createSession("form.pdf");
// Find specific form fields by name
List<FormField> signatureFields = pdf.selectFormFieldsByName("signature");
List<FormField> nameFields = pdf.selectFormFieldsByName("applicant_name");
List<FormField> dateFields = pdf.selectFormFieldsByName("application_date");
// Check and modify field values
if (!signatureFields.isEmpty()) {
FormField sig = signatureFields.get(0);
System.out.println("Signature value: " + sig.getValue());
sig.edit().value("John Doe").apply();
}
Combining Selection Methods
You can chain and combine selection methods to create complex queries:
- Python
- TypeScript
- Java
from pdfdancer import PDFDancer
with PDFDancer.open("invoice.pdf") as pdf:
# Find all invoices on first page
invoices = pdf.page(1).select_paragraphs_starting_with("Invoice #")
# Find all dollar amounts
prices = pdf.select_paragraphs_matching(r"\$\d+\.\d{2}")
# Find signature field and check if signed
sig_fields = pdf.select_form_fields_by_name("signature")
if sig_fields and sig_fields[0].value:
print("Document is signed")
# Delete all images on page 2
for img in pdf.page(2).select_images():
img.delete()
pdf.save("processed.pdf")
import { PDFDancer } from 'pdfdancer-client-typescript';
const pdf = await PDFDancer.open('invoice.pdf');
// Find all invoices on first page
const invoices = await pdf.page(1).selectParagraphsStartingWith('Invoice #');
// Find all dollar amounts
const prices = await pdf.selectParagraphsMatching('\\$\\d+\\.\\d{2}');
// Find signature field and check if signed
const sigFields = await pdf.selectFormFieldsByName('signature');
if (sigFields.length > 0 && sigFields[0].value) {
console.log('Document is signed');
}
// Delete all images on page 2
const images = await pdf.page(2).selectImages();
for (const img of images) {
await img.delete();
}
await pdf.save('processed.pdf');
import com.tfc.pdf.pdfdancer.api.PDFDancer;
import com.tfc.pdf.pdfdancer.api.common.model.*;
PDFDancer pdf = PDFDancer.createSession("invoice.pdf");
// Find all invoices on first page
List<Paragraph> invoices = pdf.page(1).selectParagraphsStartingWith("Invoice #");
// Find all dollar amounts
List<Paragraph> prices = pdf.selectParagraphsMatching("\\$\\d+\\.\\d{2}");
// Find signature field and check if signed
List<FormField> sigFields = pdf.selectFormFieldsByName("signature");
if (!sigFields.isEmpty() && sigFields.get(0).getValue() != null) {
System.out.println("Document is signed");
}
// Delete all images on page 2
for (Image img : pdf.page(2).selectImages()) {
img.delete();
}
pdf.save("processed.pdf");
Convenience Methods: Select First Match
All multi-result selection methods (select_paragraphs_*, select_text_lines_*, etc.) return arrays/lists. For convenience, singular versions are available that return just the first match (or null/None if no matches found).
When to Use Singular Methods
Use singular selection methods when you:
- Know there's only one match expected
- Only need the first occurrence
- Want to avoid index access (
results[0])
- Python
- TypeScript
- Java
from pdfdancer import PDFDancer
with PDFDancer.open("invoice.pdf") as pdf:
# Plural: returns list (may be empty)
headers = pdf.select_paragraphs_starting_with("Invoice #")
if headers:
first_header = headers[0]
# Singular: returns first match or None
first_header = pdf.select_paragraph_starting_with("Invoice #")
if first_header:
print(f"Invoice number: {first_header.text}")
const pdf = await PDFDancer.open('invoice.pdf');
// Plural: returns array (may be empty)
const headers = await pdf.selectParagraphsStartingWith('Invoice #');
if (headers.length > 0) {
const firstHeader = headers[0];
}
// Singular: returns first match or null
const firstHeader = await pdf.selectParagraphStartingWith('Invoice #');
if (firstHeader) {
console.log(`Invoice number: ${firstHeader.getText()}`);
}
PDFDancer pdf = PDFDancer.createSession("invoice.pdf");
// Plural: returns List (may be empty)
List<Paragraph> headers = pdf.selectParagraphsStartingWith("Invoice #");
if (!headers.isEmpty()) {
Paragraph firstHeader = headers.get(0);
}
// Singular: returns Optional
Optional<Paragraph> firstHeader = pdf.selectParagraphStartingWith("Invoice #");
firstHeader.ifPresent(header ->
System.out.println("Invoice number: " + header.getText())
);
Available Singular Methods
| Plural Method | Singular Method | Return Type |
|---|---|---|
select_paragraphs() | select_paragraph() | First paragraph or null/None/Optional.empty() |
select_paragraphs_starting_with(text) | select_paragraph_starting_with(text) | First match or null/None/Optional.empty() |
select_paragraphs_matching(pattern) | select_paragraph_matching(pattern) | First match or null/None/Optional.empty() |
select_paragraphs_at(x, y) | select_paragraph_at(x, y) | First match or null/None/Optional.empty() |
select_text_lines() | select_text_line() | First text line or null/None/Optional.empty() |
select_text_lines_starting_with(text) | select_text_line_starting_with(text) | First match or null/None/Optional.empty() |
select_text_lines_matching(pattern) | select_text_line_matching(pattern) | First match or null/None/Optional.empty() |
select_text_lines_at(x, y) | select_text_line_at(x, y) | First match or null/None/Optional.empty() |
Java returns Optional<T> for singular methods, following Java best practices:
pdf.selectTextLineMatching("\\d{3}-\\d{4}")
.ifPresent(line -> System.out.println(line.getText()));
Python returns None and TypeScript returns null when no matches are found. Always check before using:
line = pdf.select_text_line_matching(r"\d{3}-\d{4}")
if line: # Check for None
print(line.text)
Selection Method Summary
By Content Type
| Content Type | All | By Text/Name | By Pattern | At Coordinates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paragraphs | select_paragraphs() | select_paragraphs_starting_with() | select_paragraphs_matching() | select_paragraphs_at() |
| Text Lines | select_text_lines() | select_text_lines_starting_with() | select_text_lines_matching() | select_text_lines_at() |
| Images | select_images() | — | — | select_images_at() |
| Form Fields | select_form_fields() | select_form_fields_by_name() | — | select_form_fields_at() |
| Form XObjects | select_forms() | — | — | select_forms_at() |
| Paths | select_paths() | — | — | select_paths_at() |
Scope
All selection methods work at two levels:
- Document-level:
pdf.select_*()- searches across all pages - Page-level:
pdf.page(pageNumber).select_*()- searches only on specified page
Next Steps
- Working with Text – Edit and manipulate selected text
- Working with Images – Manipulate selected images
- Working with AcroForms – Fill and update form fields
- Working with Vector Graphics – Work with paths
- Positioning – Understand coordinate systems for selection